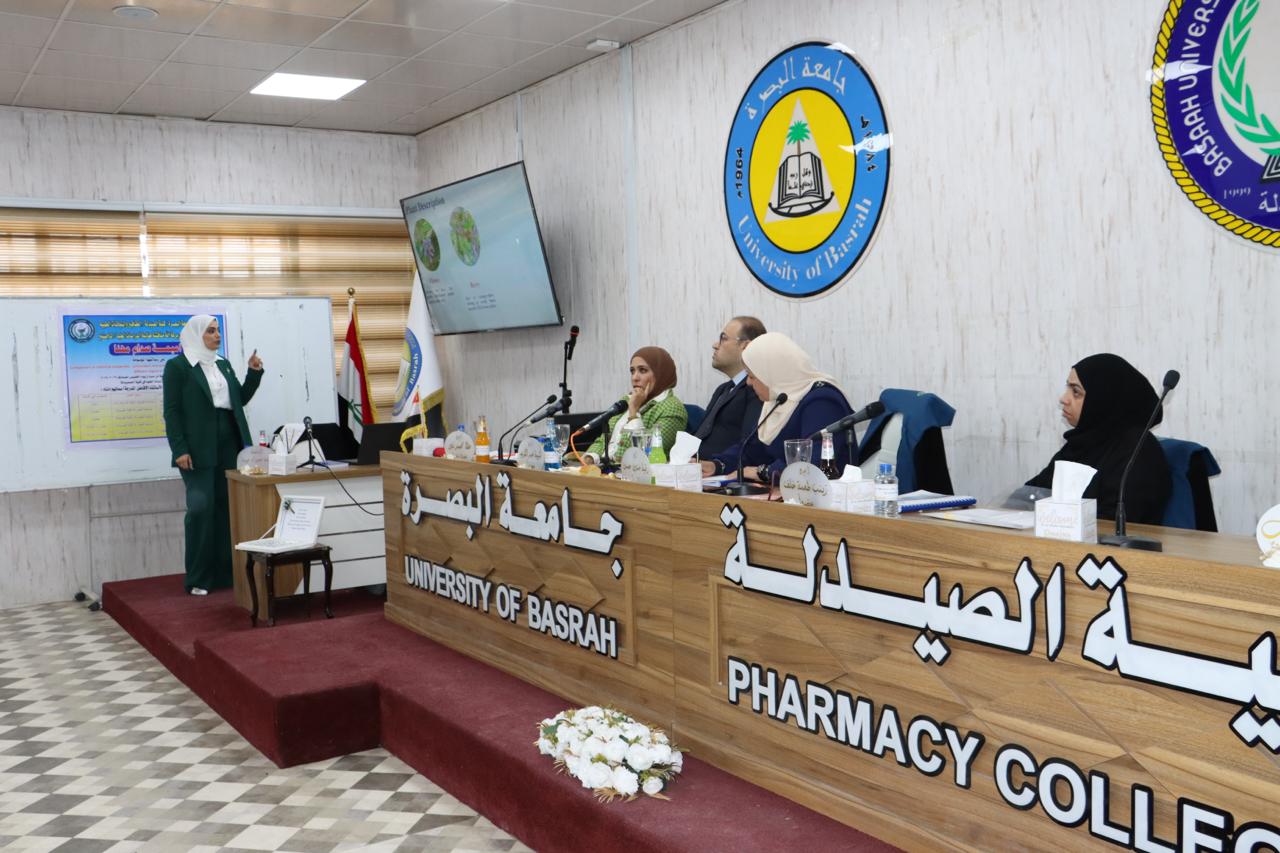
A master’s thesis at the College of Pharmacy at the University of Basrah (comparing the chemical properties, antioxidants, and anti-aging properties of the bramble plant, which was collected from different regions in Iraq).
Researcher Omaima Saddam Muhanna’s thesis included studying the ability of the plant extract to act as an antioxidant and anti-aging agent. The plant extracts (12 samples) were examined by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify the compounds present in the plant samples and compare them depending on the regions, parts of the plant, and method of extraction. The results showed that all samples contained biologically important chemicals, including phenols, terpenoids, ketones, and other compounds. The compounds identified in the samples included; Palmitic acid, stearic acid, and acetic acid, where the lutein concentration was determined in 12 samples using high-performance liquid chromatography.
The results showed that both leaf and fruit extracts contain lutein, but in different concentrations, as the leaf extract contained a higher concentration than the fruit extract. The leaf extract collected from Basra and extracted using the re-soaking method showed the highest concentration of lutein, which amounted to 13.55 mg/ml, while The fruits collected from Baghdad and extracted using ultrasound contained the lowest concentration of lutein, which was 1.74 mg/ml.
.jpeg)