The Pharmacology and Toxicology Department at the College of Pharmacy at the University of Basrah organized a seminar entitled (Interactions between drugs and medicinal herbs).
The discussion panel included a lecture given by lecturer Shaima Nadem, in which she explained that the use of herbal supplements has a long history - dating back thousands of years. Examples of important drugs extracted from plants include reserpine, morphine, penicillin, and the anti-cancer drug Vinca alkaloid, which can be purchased over the counter (OTC) and today may be classified as “all natural.” The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not apply the same efficacy and safety studies used for pharmaceuticals. Description of herbs and nutritional supplements and their manufacturers.
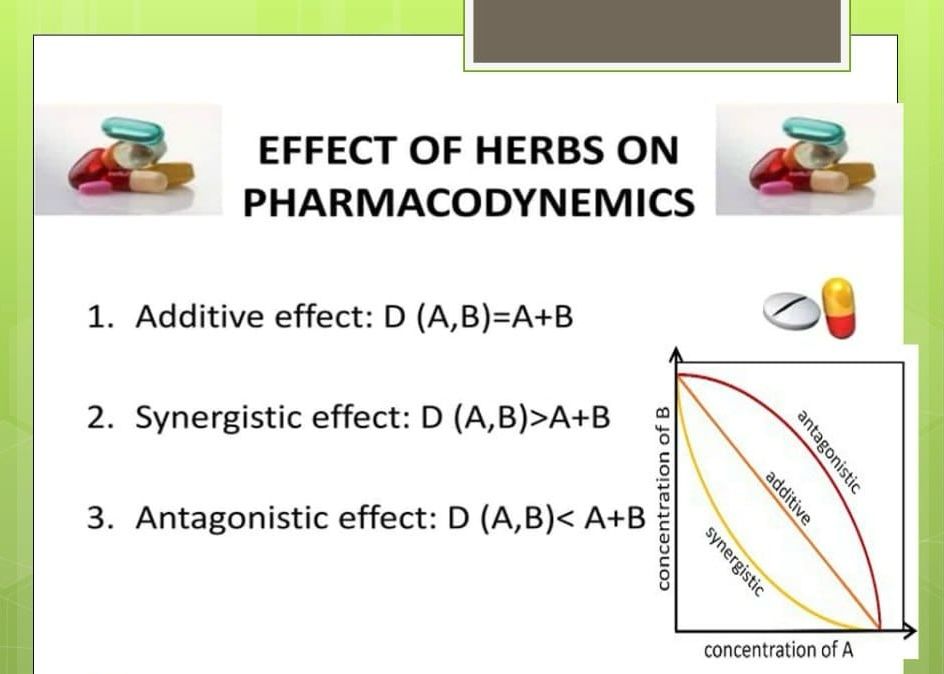
The lecturer added that herbal supplements may be from plant or herbal sources, but the active ingredients can still be strong chemicals. For this reason, herbal supplements can have drug interactions, even with each other or with medications. These products are not labeled with safety warnings, and it is difficult for the consumer to know if an interaction may occur.
The lecture aimed to raise awareness that taking herbs together will make most people, especially the elderly, suffer from some chronic diseases such as diabetes, blood pressure, and heart diseases. This requires continuing to use non-herbal medicines constantly. Some medical studies and research have recorded hundreds of very serious cases resulting from the interaction of herbs and medicines. Chemicals, and health organizations have warned of the danger of these interactions to human health. Research centers have also confirmed the danger of the gross lack of knowledge about the harmful interactions between herbs and chemical medicines. At the forefront of the dangerous interactions between herbs and chemical medicines is the interaction of some herbs that prevent blood clotting, such as garlic, ginger, and the plant. Ginkgo with chemical medications that increase blood fluidity, such as aspirin, and this interaction may lead to severe bleeding that may kill the patient, and many other interactions.